Recognizing and Treating Ear Hematomas in Dogs
Ear hematomas are painful, fluid-filled swellings that form between the layers of a dog’s ear flap. If left untreated, they can cause discomfort, scarring, and long-term deformity. While not life-threatening, ear hematomas require prompt veterinary attention to relieve pain and prevent complications.
At Providence Veterinary Clinic in Virginia Beach, we are dedicated to helping pet owners recognize and treat ear hematomas effectively. This guide will explain what causes them, how to identify them, and what treatment options are available.
What Is an Ear Hematoma?
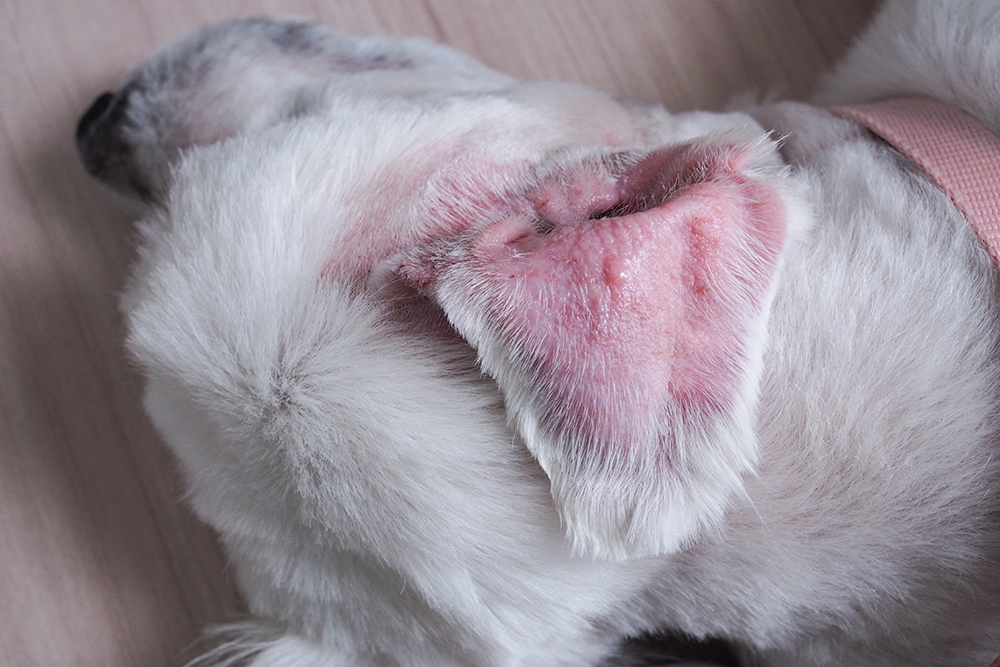
An aural hematoma occurs when blood collects between the skin and cartilage of a dog’s ear flap (pinna). This buildup creates a soft, swollen, and often painful lump.
The American College of Veterinary Surgeons (ACVS) explains that ear hematomas develop when small blood vessels rupture due to head shaking, scratching, or trauma.
What Causes Ear Hematomas in Dogs?
Common Causes of Ear Hematomas:
1. Ear Infections and Allergies
- Ear infections cause inflammation, itching, and head shaking, increasing the risk of hematomas.
- Allergies can lead to chronic ear irritation, making dogs more likely to scratch or shake their heads excessively.
- Learn about dog allergies and their role in ear problems from the American Kennel Club (AKC).
2. Head Shaking and Trauma
- Dogs that violently shake their heads or scratch their ears (due to infection, mites, or irritation) can rupture small blood vessels, leading to a hematoma.
3. Foreign Objects or Parasites
- Grass seeds, dirt, or ear mites can cause persistent ear irritation, prompting dogs to scratch aggressively, resulting in hematomas.
4. Underlying Medical Conditions
- Coagulation disorders or immune-related diseases can make dogs prone to spontaneous hematomas.
Signs of an Ear Hematoma
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Swelling of the ear flap (soft, fluid-filled, or firm depending on severity)
- Pain or sensitivity when touched
- Frequent head shaking or scratching
- Holding the ear at an unusual angle
- Red or warm ear flap
If you notice these signs, schedule a veterinary visit immediately. Early intervention prevents worsening pain and permanent ear deformities.
How Are Ear Hematomas Diagnosed?
Veterinarians diagnose ear hematomas through:
- Physical Examination: Checking for swelling, pain, and infection signs.
- Aspiration (Needle Test): Extracting fluid to confirm a hematoma and rule out abscesses or tumors.
- Ear Exam & Cytology: Identifying ear infections, mites, or allergies as the root cause.
The Washington State University Veterinary Hospital provides detailed insights into proper ear examination and medication techniques.
Treatment Options for Ear Hematomas
Treatment depends on the hematoma’s size, severity, and underlying cause.
1. Draining the Hematoma (Temporary Relief)
- A veterinarian may use a needle to drain the fluid, but recurrence is common unless the underlying cause is addressed.
2. Surgery (Best Long-Term Solution)
- Surgical drainage and suturing provide the most effective and permanent
- A small incision is made to remove fluid and prevent re-accumulation.
- The ear flap is sutured in place to allow proper healing.
3. Medication & Anti-Inflammatory Treatment
- Steroids or anti-inflammatory drugs help reduce swelling.
- Antibiotics are used if an infection is present.
- Ear cleaning and allergy treatment help prevent recurrence.
- Learn how to properly clean your dog’s ears to prevent infections from Cornell University’s Riney Canine Health Center.
4. No Treatment (Not Recommended)
- If left untreated, the hematoma may slowly resolve but will likely result in scar tissue and a deformed “cauliflower ear”.
Read more about treatment options from the AKC’s guide to ear hematomas.
How to Prevent Ear Hematomas
- Regular Ear Cleaning & Exams: Prevent infections and catch issues early.
- Address Underlying Allergies: Work with your vet to identify and manage allergens.
- Avoid Hard Shaking & Scratching: If your dog frequently shakes or scratches, check for signs of irritation.
- Use Vet-Approved Ear Cleaners: Avoid using cotton swabs, which can push debris deeper into the ear canal.
At Providence Veterinary Clinic, we provide comprehensive ear care, allergy management, and surgical solutions for ear hematomas.
Concerned about your dog’s ears? Contact us today for expert advice and treatment options.
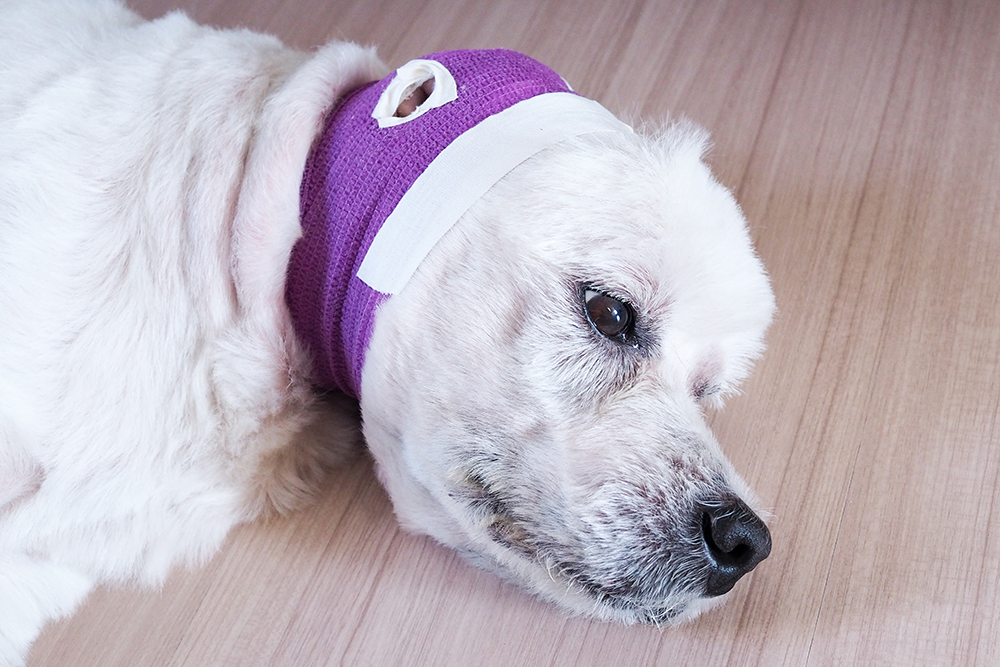

Acting Fast to Prevent Complications
Ear hematomas are painful but treatable—the key is early intervention. If your dog shows signs of ear swelling or discomfort, seek veterinary care before the condition worsens.
At Providence Veterinary Clinic, we offer:
- Accurate diagnosis & treatment for ear hematomas
- Customized care plans for allergies and infections
- Surgical and non-surgical options tailored to your pet’s needs
Book an appointment today: Schedule a Visit
Meet our expert team: Learn More




Leave A Comment