Pets can suffer from various skin conditions, leading to discomfort, infection, hair loss, and serious health issues if left untreated. Learn to identify common skin conditions in your furry pal so you can get them the treatment they need to look and feel their best. Our Providence Vet team describes some of the most common skin conditions we treat and how you can prevent them in your furry friend.
Skin infections in pets
Skin infections in pets can be caused by bacteria or yeast, often resulting from underlying issues such as allergies, wounds, or parasites. Pets with skin infections may exhibit redness, swelling, oozing sores, hair loss, and a foul odor. Treatment typically involves oral or topical antibiotics or antifungal medications. Additionally, you need to keep the affected area clean and dry. Preventing skin infections includes regular grooming, promptly addressing any wounds or injuries, and managing underlying conditions that could predispose your pet to infections.
Allergic dermatitis in pets
Allergic dermatitis is a reaction to allergens in food, in the environment, including pollen or dust, or in flea saliva. Pets suffering from allergic dermatitis often experience intense itching, red and inflamed skin, chronic ear infections, and hair loss. Allergen identification is essential for managing your four-legged friend’s allergies. Treatments include antihistamines, steroids, or other medications to control allergies, as well as dietary changes, parasite prevention, and regular bathing with medicated shampoos to soothe irritated skin. Allergy shots can benefit pets affected by environmental allergies.
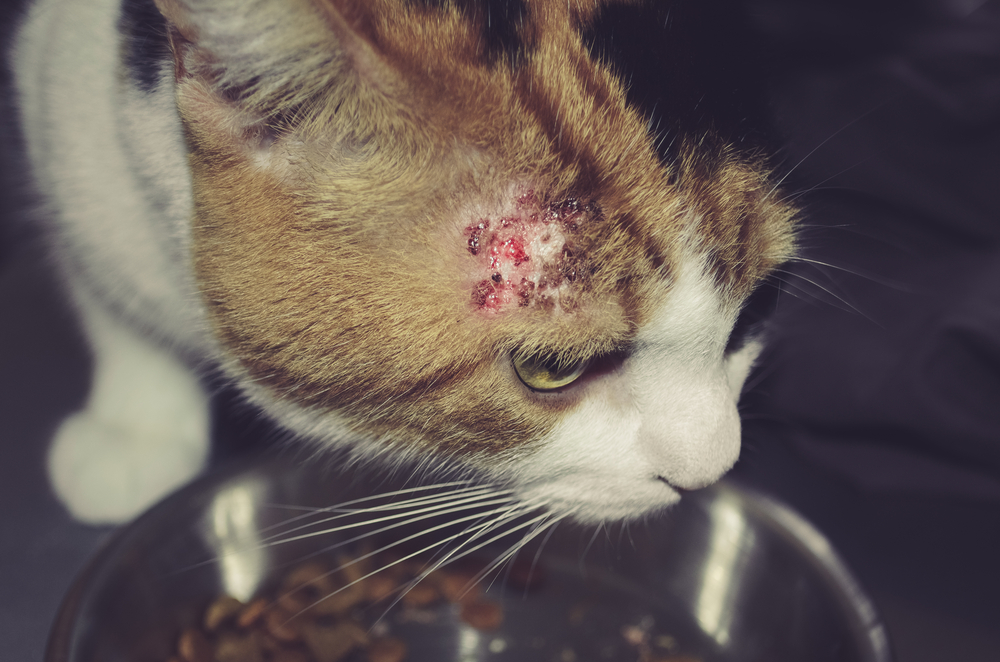
Hot spots in pets
Hot spots, also known as acute moist dermatitis, are inflamed and infected skin areas that can appear suddenly and spread quickly. Signs include red, oozing sores that can become crusty, intense itching and licking, and hair loss around the affected area. Treatment involves gently clipping away the fur, cleaning the hot spot with an antiseptic solution, administering antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications if necessary, and using an Elizabethan collar (i.e., e-collar) to prevent the affected pet from licking the area. Our Providence Vet team must also address any underlying causes, such as flea infestations or allergies, to prevent recurrence.
Ringworm in pets
Despite its name, ringworm is not a worm but a fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. Pets with ringworm often exhibit circular patches of hair loss, scaly or crusty skin, and mild itching. Treatment includes topical antifungal creams and ointments, oral medications for more severe cases, and environmental cleaning to prevent reinfection. Ringworm is an infectious condition that can be transmitted between pets and people, so avoid sharing items, such as bedding, toys, and grooming tools, with infected pets.
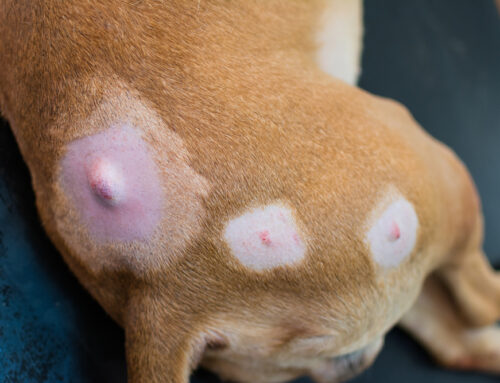
Mange in pets
Mange is caused by mites that burrow into the skin, leading to severe itching and discomfort. The two main mange types are sarcoptic mange (i.e., scabies) and demodectic mange. Sarcoptic mange is contagious and can be transmitted between pets and people, whereas demodectic mange typically occurs in young or immunocompromised pets. Mange signs include intense itching, patchy hair loss, red and inflamed skin that can become crusty and scabbed, and secondary infections caused by constant scratching and open sores. Treatment involves oral or topical medications to kill the mites and medicated shampoos to soothe the skin and remove mites.
Alopecia in pets
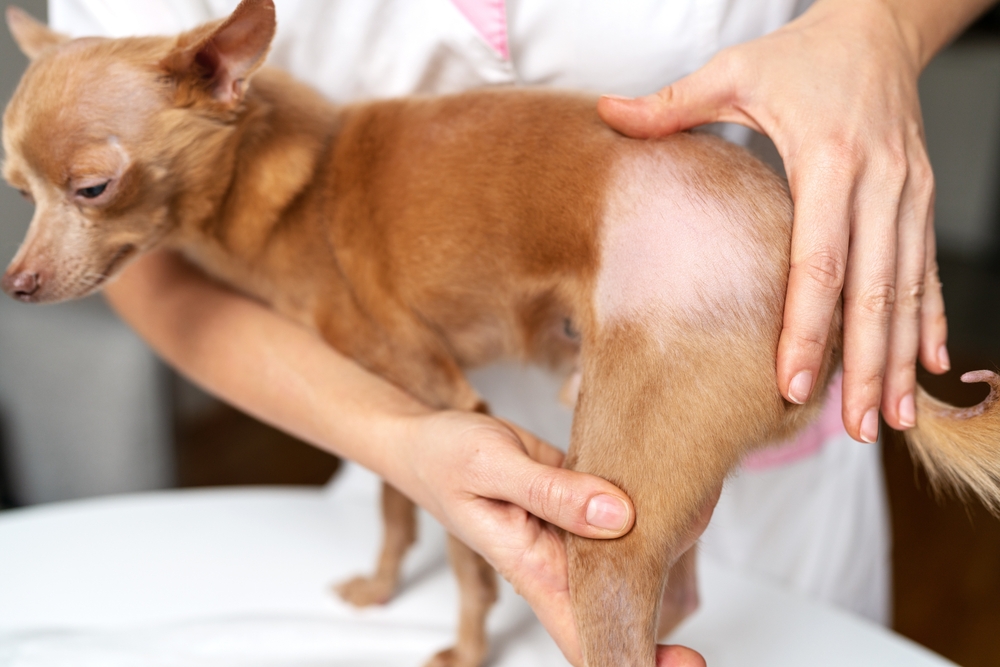

Alopecia—hair loss—is a common condition in pets that can have various causes. This condition can be localized, affecting small skin patches, or generalized, spreading over large areas. Alopecia causes include allergies, hormonal imbalances, infections, parasites, and underlying health issues. Pets with alopecia may have bald patches, thinning fur, or inflamed or scaly skin, and they often lick, scratch, and chew excessively.
Alopecia treatment depends on the condition’s underlying cause. For example, if allergies are to blame, managing your pet’s exposure to their allergens and administering allergy medications may help. Hormonal imbalances may require hormone replacement therapies or other medications. If a pet has an infection or parasites, appropriate antimicrobial or antiparasitic treatments are necessary. Additionally, a nutritious diet and regular grooming can support overall skin and coat health, potentially preventing alopecia.
Maintaining your pet’s skin health is crucial for their overall well-being. Regular grooming, a balanced diet, and routine veterinary checkups are key to preventing many of these issues. If you notice any unusual skin changes in your furry pal, schedule an appointment with our Providence Vet team.




Leave A Comment